Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 SiO
SiO glass made by a method for containerless supercooled-liquid-phase processing at high temperatures
glass made by a method for containerless supercooled-liquid-phase processing at high temperaturesKohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Takeuchi, Ken*
Mirai Zairyo, 5(4), p.28 - 33, 2005/04
We succeeded in producing highly pure glass made of "forsterite," contained in upper mantle of the Earth and meteorites. Although ordinary glass is made of silica network structure, this glass has an unsymmetrical network structure of magnesium oxide polyhedrons, which is deemed to destroy the silica network structure. We produced glass with extremely rare impurities by melting forsterite while floating it with inert gas and sound waves and then quenching it while holding it in an approximate microgravity condition equivalent to space. Development of a new optical fiber and improvement and cost reduction of operating equipment, such as operation laser, because high-purity glass can be produced using materials, which has been deemed to be appropriate.
Kohara, Shinji*; Oishi, Yasuo*; Takata, Masaki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Suzuya, Kentaro
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 47(2), p.123 - 129, 2005/04
The use of high-energy (E  50 keV) X-rays from SPring-8 allows us to perform X-ray diffraction experiments on disordered materials with the following advantages: high resolution in real space due to the wide range of scattering vector, small correction terms (particularly the absorption correction), and fast diffraction measurement with small amount of samples. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed neutron source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than has hitherto been available. Furthermore, the use of reverse Monte Carlo modelling and PDF (pair distribution function) simulation based on high-energy X-ray diffraction data have succeeded in illustrating 3-dimensional structure of disordered materials and disorder in crystalline materials.
50 keV) X-rays from SPring-8 allows us to perform X-ray diffraction experiments on disordered materials with the following advantages: high resolution in real space due to the wide range of scattering vector, small correction terms (particularly the absorption correction), and fast diffraction measurement with small amount of samples. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed neutron source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than has hitherto been available. Furthermore, the use of reverse Monte Carlo modelling and PDF (pair distribution function) simulation based on high-energy X-ray diffraction data have succeeded in illustrating 3-dimensional structure of disordered materials and disorder in crystalline materials.
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Takeuchi, Ken*
Nihon Maikurogurabiti Oyo Gakkai-Shi, 22(2), p.100 - 104, 2005/04
Forsterite Mg SiO
SiO exhibits an orthorhombic structure consisted of two kinds of MgO
exhibits an orthorhombic structure consisted of two kinds of MgO octahedra. Given only 33.3 mol% of SiO
octahedra. Given only 33.3 mol% of SiO in the material, the SiO
in the material, the SiO tetrahedra are isolated within the framework, sharing the O-O bonds with the common edges of the MgO
tetrahedra are isolated within the framework, sharing the O-O bonds with the common edges of the MgO octahedra. If forsterite can be vitrified, an interesting question concerning the glass structure arises because there is insufficient glass forming SiO
octahedra. If forsterite can be vitrified, an interesting question concerning the glass structure arises because there is insufficient glass forming SiO to establish the corner-sharing SiO
to establish the corner-sharing SiO tetrahedral network needed in conventional silicate glasses. A bulk Mg
tetrahedral network needed in conventional silicate glasses. A bulk Mg SiO
SiO glass was synthesized using an aero-acoustic levitation technique and to determine the short- to intermediate-range structure by a combined high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo computer simulation. Interestingly, we found that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing ionic magnesium species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen.
glass was synthesized using an aero-acoustic levitation technique and to determine the short- to intermediate-range structure by a combined high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction and reverse Monte Carlo computer simulation. Interestingly, we found that the role of network former is largely taken on by corner- and edge-sharing ionic magnesium species that adopt 4-, 5- and 6-coordination with oxygen.
 and GeO
and GeO
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 17(5), p.S77 - S86, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:82 Percentile:90.9(Physics, Condensed Matter)The total structure factors, S(Q), obtained from high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements on vitreous SiO (v-SiO
(v-SiO ) and vitreous GeO
) and vitreous GeO (v-GeO
(v-GeO ) have been analysed by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique to generate a three-dimensional structural model. The bond angle distributions and the ring size distributions from the model indicated that the sixfold ring and six- and sevenfold rings are dominant in v-SiO
) have been analysed by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique to generate a three-dimensional structural model. The bond angle distributions and the ring size distributions from the model indicated that the sixfold ring and six- and sevenfold rings are dominant in v-SiO and v-GeO
and v-GeO , respectively. However, the fraction of threefold rings of Ge in v-GeO
, respectively. However, the fraction of threefold rings of Ge in v-GeO is larger than that of Si in v-SiO
is larger than that of Si in v-SiO glass. These features are consistent with the published neutron diffraction and Raman scattering studies.
glass. These features are consistent with the published neutron diffraction and Raman scattering studies.
Suzuya, Kentaro
Hamon, 13(1), p.51 - 55, 2003/01
With the arrival of the latest generation of synchrotron sources and the introduction of advanced insertion devices, the high-energy (E  30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO
30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO , B
, B O
O , and GeO
, and GeO by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
Matsumoto, Kazuhiko*; Hagiwara, Rika*; Ito, Yasuhiko*; Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 199, p.29 - 33, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)The structure of 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bifluoride (EMImF HF) melt has been analyzed at 333 K by a high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction method. The total correlation function of the EMImF
HF) melt has been analyzed at 333 K by a high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction method. The total correlation function of the EMImF HF melt was similar to that of the solid state, indicating that not only the short-range but also the intermediate-range ordering in the solid are partially preserved in the liquid state. The intra-molecular F-F correlation in the anions clearly appears in the total correlation function of the EMImF
HF melt was similar to that of the solid state, indicating that not only the short-range but also the intermediate-range ordering in the solid are partially preserved in the liquid state. The intra-molecular F-F correlation in the anions clearly appears in the total correlation function of the EMImF HF melt, whereas prominent peaks are not observed in the case of a room temperature molten salt, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluorohydrogenate (EMImF
HF melt, whereas prominent peaks are not observed in the case of a room temperature molten salt, 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium fluorohydrogenate (EMImF 2.3HF).
2.3HF).
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 199, p.23 - 28, 2003/01
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:88.67(Instruments & Instrumentation)With the arrival of the latest generation of synchrotron sources and the introduction of advanced insertion devices (wigglers and undulators), the high-energy (E  30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. High-energy X-ray diffraction has several advantages: higher resolution in real space due to a wide range of scattering vector Q, smaller correction terms (especially the absorption correction), reduction of truncation errors, the feasibility of running under extreme environments, including high-temperatures and high-pressures, and the ability to make direct comparisons between X-ray and neutron diffraction data. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available.
30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. High-energy X-ray diffraction has several advantages: higher resolution in real space due to a wide range of scattering vector Q, smaller correction terms (especially the absorption correction), reduction of truncation errors, the feasibility of running under extreme environments, including high-temperatures and high-pressures, and the ability to make direct comparisons between X-ray and neutron diffraction data. Recently, high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available.
Hagiwara, Rika*; Matsumoto, Kazuhiko*; Tsuda, Tetsuya*; Ito, Yasuhiko*; Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Matsumoto, Hajime*; Miyazaki, Yoshinori*
Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 312-314, p.414 - 418, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:85.82(Materials Science, Ceramics)The structures of a series of XF 2.3HF (X= 1-methylimidazolium (MI), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMI), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium (BMI), 1-hexyl-3-methyl-imidazolium (HMI)) room temperature molten salts have been investigated by high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction technique. The correlation peaks appeared in the total correlation function are mainly ascribed to intra-molecular correlation of alkylimidazolium cations. However, it is suggested that the peak at around 3.6
2.3HF (X= 1-methylimidazolium (MI), 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium (EMI), 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium (BMI), 1-hexyl-3-methyl-imidazolium (HMI)) room temperature molten salts have been investigated by high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction technique. The correlation peaks appeared in the total correlation function are mainly ascribed to intra-molecular correlation of alkylimidazolium cations. However, it is suggested that the peak at around 3.6 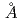 is ascribed not only to intra-molecular but also inter-molecular correlation of the cation. The contribution of the latter is also supported by the first sharp diffraction peak of the total structure factor found at almost the same position as that of a Bragg peak in the simulated X-ray diffraction pattern of solid EMIF
is ascribed not only to intra-molecular but also inter-molecular correlation of the cation. The contribution of the latter is also supported by the first sharp diffraction peak of the total structure factor found at almost the same position as that of a Bragg peak in the simulated X-ray diffraction pattern of solid EMIF HF with a layered structure, corresponding to the layer separation of
HF with a layered structure, corresponding to the layer separation of
Suzuya, Kentaro; Kohara, Shinji*
Materia, 41(3), p.206 - 215, 2002/03
With the arrival of the latest generation of synchrotron sources and the introduction of advanced insertion devices, the high-energy (E  30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO
30 keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of network forming glasses, SiO , B
, B O
O , and GeO
, and GeO by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
by the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Physics and Chemistry of Glasses, Vol.43C 2002, p.51 - 54, 2002/00
With the arrival of the latest generation of synchrotron sources and the introduction of advanced insertion devices, the high-energy (E  30keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of a typical network forming glass, silica (SiO
30keV) X-ray diffraction technique has become feasible, leading to new approaches in the quantitative study of the structure of disordered materials. Recently, the high-energy X-ray diffraction data have been combined with neutron diffraction data from a pulsed source to provide more detailed and reliable structural information than that hitherto available. We have developed a two-axis diffractometer for glass, liquid and amorphous materials at the SPring-8 high-energy X-ray diffraction beamline BL04B2. Furthermore, we have succeeded to analyze the intermediate-range order of a typical network forming glass, silica (SiO ), by reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
), by reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique with special focused on the ring structures using both high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data.
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Hoshako, 14(5), p.365 - 375, 2001/11
no abstracts in English
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Kashihara, Yasuharu*; Matsumoto, Norimasa; Umesaki, Norimasa*; Sakai, Ichiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 467-468(Part.2), p.1030 - 1033, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:138 Percentile:99.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 O
O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro*; Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Umesaki, Norimasa*
Physics and Chemistry of Glasses, 41(5), p.282 - 285, 2000/10
no abstracts in English
Kohara, Shinji*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Ono, Hideo
Yoyuen Oyobi Koon Kogaku, 43(2), p.41 - 52, 2000/05
no abstracts in English
Yoneda, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
The bending magnet beamlines of SPring-8 can provide wide band X-rays, which critical energy is 28.9 keV. One can performs the high-energy X-ray diffraction measurements by combining X-ray focusing system of a crystal bender. We examined a coherence part in ceramics samples by using the large penetration depth of the high-energy X-rays. For example, we found structural phase transitions in (Na,K,Li)NbO and (Bi
and (Bi Na
Na )TiO
)TiO . We also applied this technique to a surrogate materials for nitride fuel of (Dy,Zr)N.
. We also applied this technique to a surrogate materials for nitride fuel of (Dy,Zr)N.
Yoneda, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
A lecture will be given on nano-scale structural analysis of ferroelectric materials using atomic pair-distribution function obtained by synchrotron high-energy X-rays. The results of local structure analyses to relaxor ferroelectrics and potassium niobate nanocrystals are discussed.
 K
K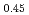 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO -based system with tetragonal structure
-based system with tetragonal structureYoneda, Yasuhiro; Takuwa, Chihaya*
no journal, ,
 K
K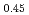 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO - Ca(Zr
- Ca(Zr Ti
Ti )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Takuwa, Chihaya*; Kobune, Masafumi*
no journal, ,
A two-body correlation distribution function obtained from high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments was applied to a niobium-based oxide ferroelectric (Na K
K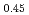 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO - Ca(Zr
- Ca(Zr Ti
Ti )O
)O with excellent piezoelectric properties. The average structure of (Na
with excellent piezoelectric properties. The average structure of (Na K
K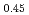 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO - Ca(Zr
- Ca(Zr Ti
Ti )O
)O changes with a small amount of Ta-additives. When the density and grain size of the sample were matched to determine whether the local structure changed with the change in the average structure, there was almost no difference in the local structure between 3
changes with a small amount of Ta-additives. When the density and grain size of the sample were matched to determine whether the local structure changed with the change in the average structure, there was almost no difference in the local structure between 3 and 10
and 10 . The difference was observed in the coherence of the nanoscale region, suggesting a difference in the ferroelectric domain size.
. The difference was observed in the coherence of the nanoscale region, suggesting a difference in the ferroelectric domain size.